How nutrients affect plants? In the growing process, tree needs nutrients for a complete growth and high quality fruits. Main nutrients which plants absorbed are in soil. However, during long-term cultivation, the soil will be gradually degraded due to many factors. As a result, fertilizer should be periodically applied. Let’s learn about this issue!
Mục lục:
What happens to plants without nutrients?
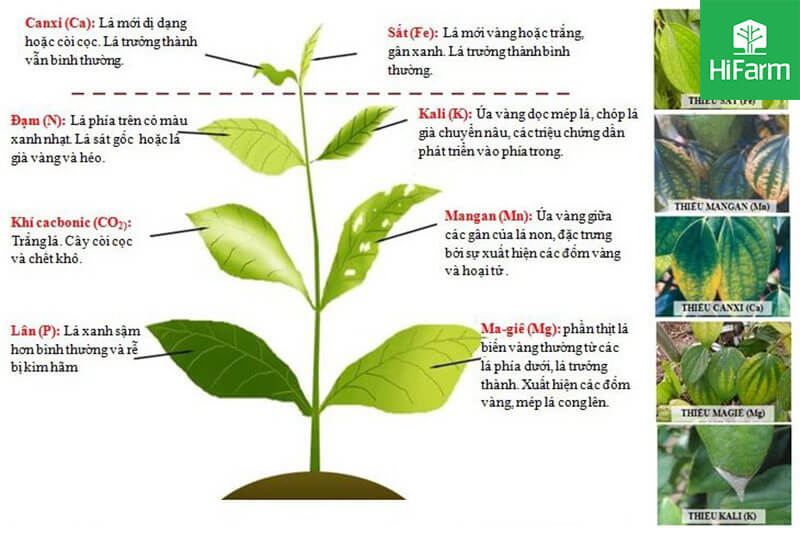
These essential nutrients directly involved in the metabolism in the body. The life cycle wouldn’t complete without them.
Nutritional elements take part in the metabolism, physiological activities, make up the living substance and increase the tolerance of the plant. They are key factors determining the productivity and quality of agricultural products.
The plant body contains many mineral elements which are present in the periodic table. They are very important and essential to the growth and development of all species. In case just one of them is missing, the nutrition balance of plant will be broken and the its life cycle couldn’t be completed
Important nutritional factors determine the yield and quality of agricultural products
Nutrition for plants
There are 3 essential nutrition groups: basic nutrients (NPK), macronutrients and micronutrients.
Basic nutrients (NPK):
- Nitrogen: indispensable nutrient for healthy plant growth, dark green leaves and effective photosynthesis.
- Phosphorus: Helps root grow strongly, enough phosphorus makes more flowers.
- Potassium: Improves overall plant health and prevents diseases.
- Calcium: Promotes root and shoot, builds cell walls.
- Magnesium: corrects other nutrients’ absorption. Furthermore, it assists in seed and chlorophyll formation.
- Sulfur: maintains a dark green color and stimulates plant growth. Sulfur is also required for the production of chlorophyll.
Trace elements:
- Boron: supports cells growth and regulates plant metabolism. Specifically, it synthesizes protein then develops into cells, metabolizes carbohydrates. More than this, it involves in sugar transposition, hormone control, pollen fertilization and fruit quantity growth.
- Chlorine: An essential substance for gas exchange, photosynthesis and protecting plants against disease.
- Copper: forms chlorophyll, activates enzymes and helps synthesize lignin.
- Iron: produces chlorophyll and other biochemical processes.
- Manganese: it’s essential for the production of chlorophyll.
- Zinc: Supports the development of enzymes and hormones. It also produces chlorophyll.
EC and TDS index
It is not easy to diagnose undernourished plants through their physical manifestations, so we usually control the nutrient content and concentration through the EC or TDS index.

What is EC?
EC stands for Electrical Conductivity, also known as electrical conductivity. EC measures a solution’s electrical conductivity. The more ions there is, the higher the conductivity is; the less ions, the lower the conductivity. EC is usually reported in milliSiemans per centimeter (mS / cm).
What is TDS?
TDS stands for Total Dissolved Solids. TDS measures all the content of organic and inorganic solids in a solution which exists in the form of molecules, particles in the form of ions or in suspension.
There are two main methods of measuring TDS: the weight-based method and the conductivity method. Measured results will be displayed in milligrams per liter (mg / L), parts per million (ppm), grams per liter (g / L) or parts per thousand (ppt).
PH concentration
Soil pH, which is also known as the reactivity of the soil, is measured by the concentration of H + and OH– ions in the soil. It has a great influence on the growth and availability of nutrients for plants. If we don’t adjust pH before fertilizing, plants will not be able to absorb nutrients or we can say that it’s wasting fertilizer.

 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt